Table Of Content
In addition to the above effects plots, Minitab calculates the coefficients and constants for response equations. The response equations can be used as models for predicting responses at different operating conditions (factors). The coefficients and constants for wt% methanol in biodiesel and number of theoretical stages are shown below. After the complete DOE study has been performed, Minitab can be used to analyze the effect of experimental results (referred to as responses) on the factors specified in the design. The first step in analyzing the results is entering the responses into the DOE table.
Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide
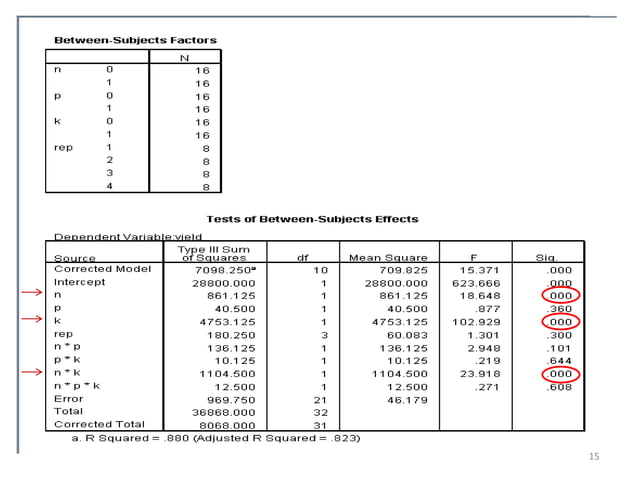
So, just looking at this summary information wouldn't tell us what to do except that we could drop the 3-way interaction. Let’s name our factors A, B and C, and use –1 and +1 for the low and high levels, respectively (Table 1). Even though there is no replication, this 23 full factorial design can detect factor effects, if some sensible assumptions are made.
Assigning Participants to Conditions
For example, people are either low in hypochondriasis or high in hypochondriasis; they cannot be tested in both of these conditions. Second, such studies are generally considered to be experiments as long as at least one independent variable is manipulated, regardless of how many non-manipulated independent variables are included. Third, it is important to remember that causal conclusions can only be drawn about the manipulated independent variable. For example, Schnall and her colleagues were justified in concluding that disgust affected the harshness of their participants’ moral judgments because they manipulated that variable and randomly assigned participants to the clean or messy room. But they would not have been justified in concluding that participants’ private body consciousness affected the harshness of their participants’ moral judgments because they did not manipulate that variable. It could be, for example, that having a strict moral code and a heightened awareness of one’s body are both caused by some third variable (e.g., neuroticism).
Non-Manipulated Independent Variables
There are many simple examples of two independent variables being dependent on one another to produce an outcome. The dependent variable (outcome that is measured) could be how far the car can drive in 1 minute. These independent variables are good examples of variables that are truly independent from one another.
Often, coding the levels as (1) low/high, (2) -/+, (3) -1/+1, or (4) 0/1 is more convenient and meaningful than the actual level of the factors, especially for the designs and analyses of the factorial experiments. These coding systems are particularly useful in developing the methods in factorial and fractional factorial design of experiments. Moreover, general formula and methods can only be developed utilizing the coding system. Often, coded levels produce smooth, meaningful and easy to understand contour plots and response surfaces. Moreover, especially in complex designs, the coded levels such as the low- and high-level of a factor are easier to understand.
How To Add Biologics Manufacturing Efficiency With Design Of Experiments Part 2 - BioProcess Online
How To Add Biologics Manufacturing Efficiency With Design Of Experiments Part 2.
Posted: Wed, 05 Apr 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Book traversal links for Lesson 5: Introduction to Factorial Designs
If a quadratic effect is expected for a factor, a more complicated experiment should be used, such as a central composite design. Optimization of factors that could have quadratic effects is the primary goal of response surface methodology. The use of a control group is an important experimental design method that involves having a group of participants that do not receive the treatment or intervention being studied. The control group is used as a baseline to compare the effects of the treatment group. The factorial design, as well as simplifying the process and making research cheaper, allows many levels of analysis. As well as highlighting the relationships between variables, it also allows the effects of manipulating a single variable to be isolated and analyzed singly.
What is a Factorial Experiment?
The third factor is an adherence factor (i.e., an automated medication counter with counseling, on/off). Thus, this experiment would address which type of NRT exerts additive or interactive effects when used with varenicline, and whether the adherence intervention exerts main or interactive effects. Obviously the investigator must make the intervention relevant to each medication type, but such adjustment raises questions. Is the adherence intervention different enough in its various forms (across medications) so that it no longer constitutes a single, coherent component? If that is true, its effects cannot be interpreted in a straightforward manner. If no adherence main effect is found, is that because this component was inconsistently delivered (adjusted for each medication)?
Normal Probability Plot for the Effects
If they were high in private body consciousness, then those in the messy room made harsher judgments. If they were low in private body consciousness, then whether the room was clean or messy did not matter. In principle, factorial designs can include any number of independent variables with any number of levels.
Visualizing Main Effects & Interaction Effects
We will start by looking at just two factors and then generalize to more than two factors. Investigating multiple factors in the same design automatically gives us replication for each of the factors. As seen above, RPM is shown with a positive effect for number of theoretical stages, but a negative effect for wt% methanol in biodiesel.
The result of this study was that the participants high in hypochondriasis were better than those low in hypochondriasis at recalling the health-related words, but they were no better at recalling the non-health-related words. In many factorial designs, one of the independent variables is a non-manipulated independent variable. Some were negative health-related words (e.g., tumor, coronary), and others were not health related (e.g., election, geometry).
In the "Modify Design" menu, users can modify factors, replicate design, randomize design, renumber design, fold design, and add axial points. To change the factors, click the "Modify factors" radio button and then "Specify" to see the following options menu. Investigators may wish to adjust ICs to enhance their compatibility with other components. For instance, investigators might choose to reduce the burden of an IC by cutting sessions or contact times. This might reduce the meaning of the factor because it might make the IC unnecessarily ineffective or unrepresentative. Researchers want to determine how the amount of sleep a person gets the night before an exam impacts performance on a math test the next day.
Simplest reaction time analysis for experimental psychology? - ResearchGate
Simplest reaction time analysis for experimental psychology?.
Posted: Fri, 29 Mar 2019 07:00:00 GMT [source]
In this section, we look at some approaches to complex correlational research that involve measuring several variables and assessing the relationships among them. The difference between red and green bars is small for level 1 of IV1, but large for level 2. The differences between the differences are different, so there is an interaction. For example, both the red and green bars for IV1 level 1 are higher than IV1 Level 2. And, both of the red bars (IV2 level 1) are higher than the green bars (IV2 level 2). Accordingly, researchers must take certain precautions both in terms of methodology and statistical analyses when interpreting complex experimental designs.
To get a mean factorial effect, the totals needs to be divided by 2 times the number of replicates, where a replicate is a repeated experiment. An example graphical representation of a factorial design of experiment is provided in Figure 1 . The factorial design of experiment is described with examples in Video 1. For example, a shrimp aquaculture experiment[9] might have factors temperature at 25°C and 35°C, density at 80 or 160 shrimp/40 liters, and salinity at 10%, 25% and 40%.
This involves systematically varying the order in which participants receive treatments or interventions in order to control for order effects. In this design, the researcher manipulates one or more variables at different levels and uses a randomized block design to control for other variables. Other than these slight detractions, a factorial design is a mainstay of many scientific disciplines, delivering great results in the field. Factorial designs are extremely useful to psychologists and field scientists as a preliminary study, allowing them to judge whether there is a link between variables, whilst reducing the possibility of experimental error and confounding variables.
So by looking at how many numbers are in the notation, you can determine how many independent variables there are in the experiment. 2 x 2, 3 x 3, and 2 x 3 designs all have two numbers in the notation and therefore all have two independent variables. The numerical value of each of the numbers represents the number of levels of each independent variable. A 2 means that the independent variable has two levels, a 3 means that the independent variable has three levels, a 4 means it has four levels, etc. To illustrate, a 3 x 3 design has two independent variables, each with three levels, while a 2 x 2 x 2 design has three independent variables, each with two levels.

No comments:
Post a Comment